Square pyramid
A square pyramid is a pyramid where the base is a quadrilateral, most often a square. The figure therefore has a total of five faces:
One square base and four triangular side faces.
If the base is a square and the apex is placed directly above the center, it is a regular square pyramid. If the apex is not centered, the pyramid is irregular.
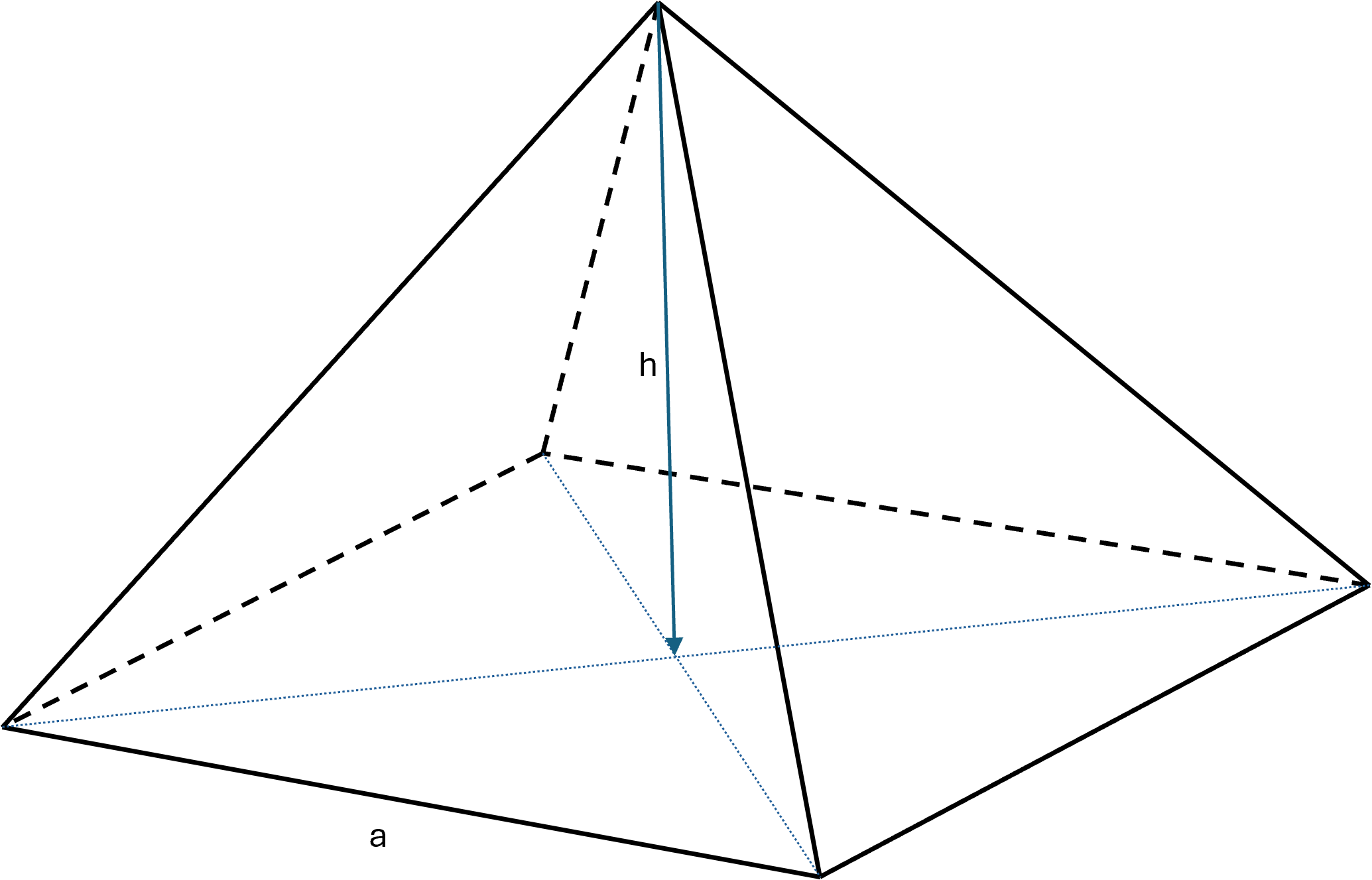
Regular square pyramid
Volume
The volume of a square pyramid is found using the general formula for pyramids:
$$ \large V = \frac{1}{3} \cdot A_{base} \cdot h $$
Since the base is a square with side length \( \large a \), we get:
$$ \large V = \frac{1}{3} \cdot a^2 \cdot h $$
Surface area
The surface area consists of the base and the four triangular side faces:
$$ \large S = a^2 + 2 \cdot a \cdot s $$
where \( \large s \) is the slant height, i.e. the height of a triangular side face.
The slant height can be calculated from the side length \( \large a \) and the height of the pyramid:
$$ \large s = \sqrt{h^2 + \left(\frac{a}{2}\right)^2} $$
Irregular square pyramid
If the base is a rectangle or another arbitrary quadrilateral, or if the apex is not above the center, the figure is called an irregular square pyramid.
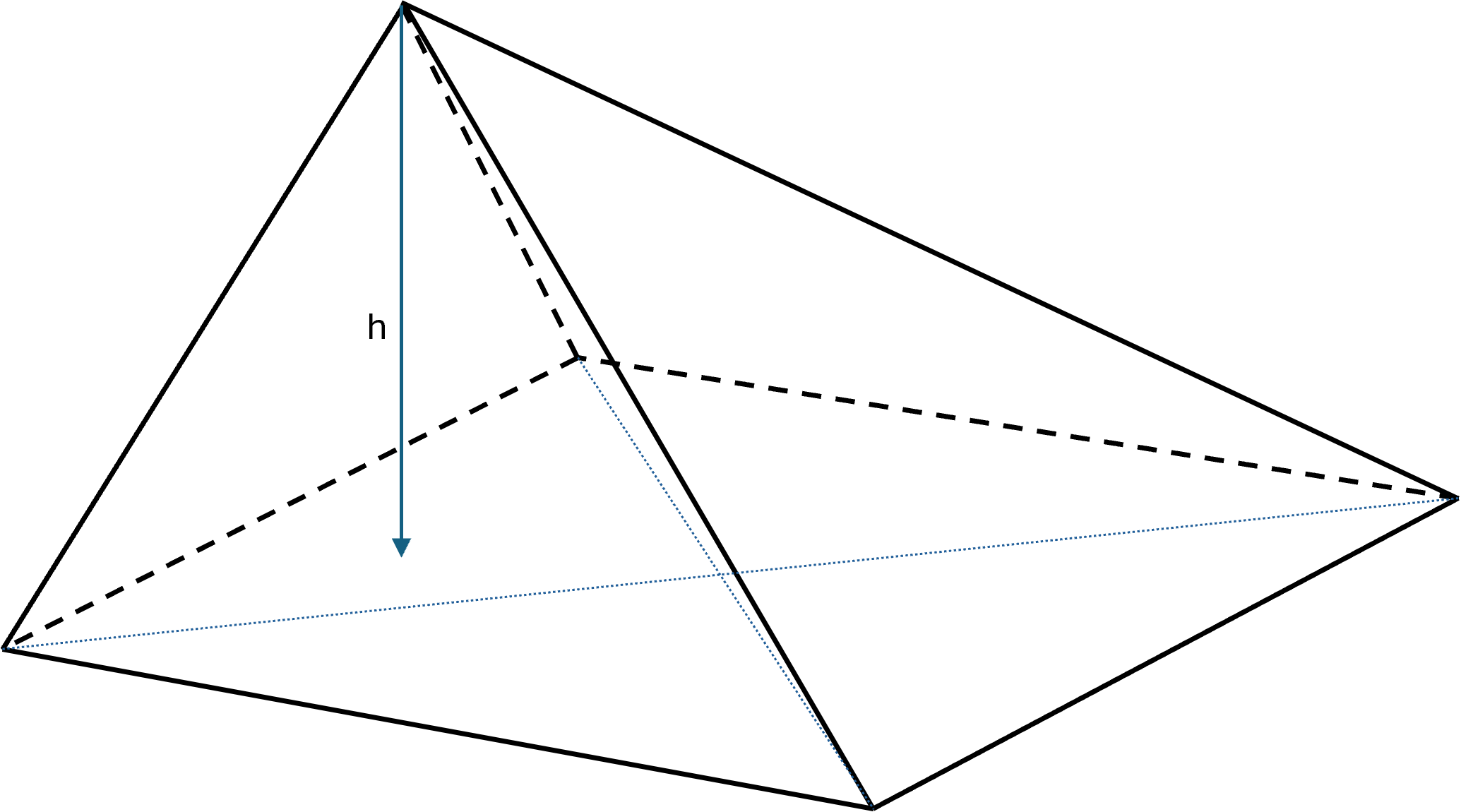
The general formulas for pyramids still apply:
$$ \large V = \frac{1}{3} \cdot A_{base} \cdot h $$
$$ \large S = A_{base} + A_{sides} $$
However, the calculation of the areas of the base and the side faces requires individual methods depending on the shape.