Cube
A cube is a three-dimensional geometric figure that has two parallel and congruent square end faces. The four other faces are also squares.
A cube is therefore a special case of a box, where all edges are equal in length. In Danish a cube is also called a die.
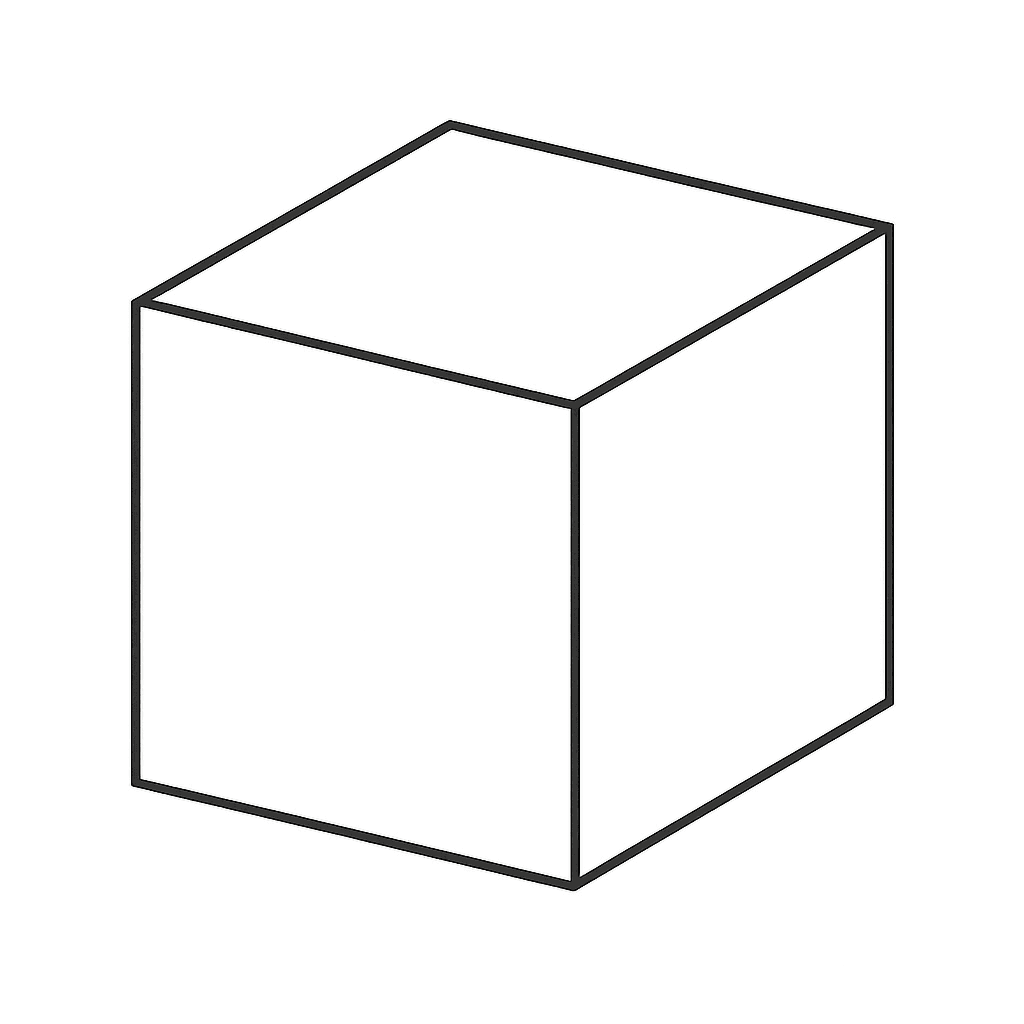
Volume
The volume of a cube is found by multiplying the side length by itself three times:
$$ \large V = a^3 $$
If the cube is oblique, then the height is not equal to the slanted edge length, but the perpendicular distance between the two square end faces. If the slanted edge is \( \large s \), and the angle to the base is \( \large \theta \), the actual height is given by:
$$ \large h = s \cdot \sin(\theta) $$
In that case the volume can also be written as the base area times the height:
$$ \large V = A_{base} \cdot h $$
$$ \large V = a^2 \cdot h $$
Example
We will calculate the volume of a cube with side length \( \large a = 5 \,\text{cm} \).
The volume is:
$$ \large V = 5^3 = 125 \,\text{cm}^3 $$
Example of an oblique cube
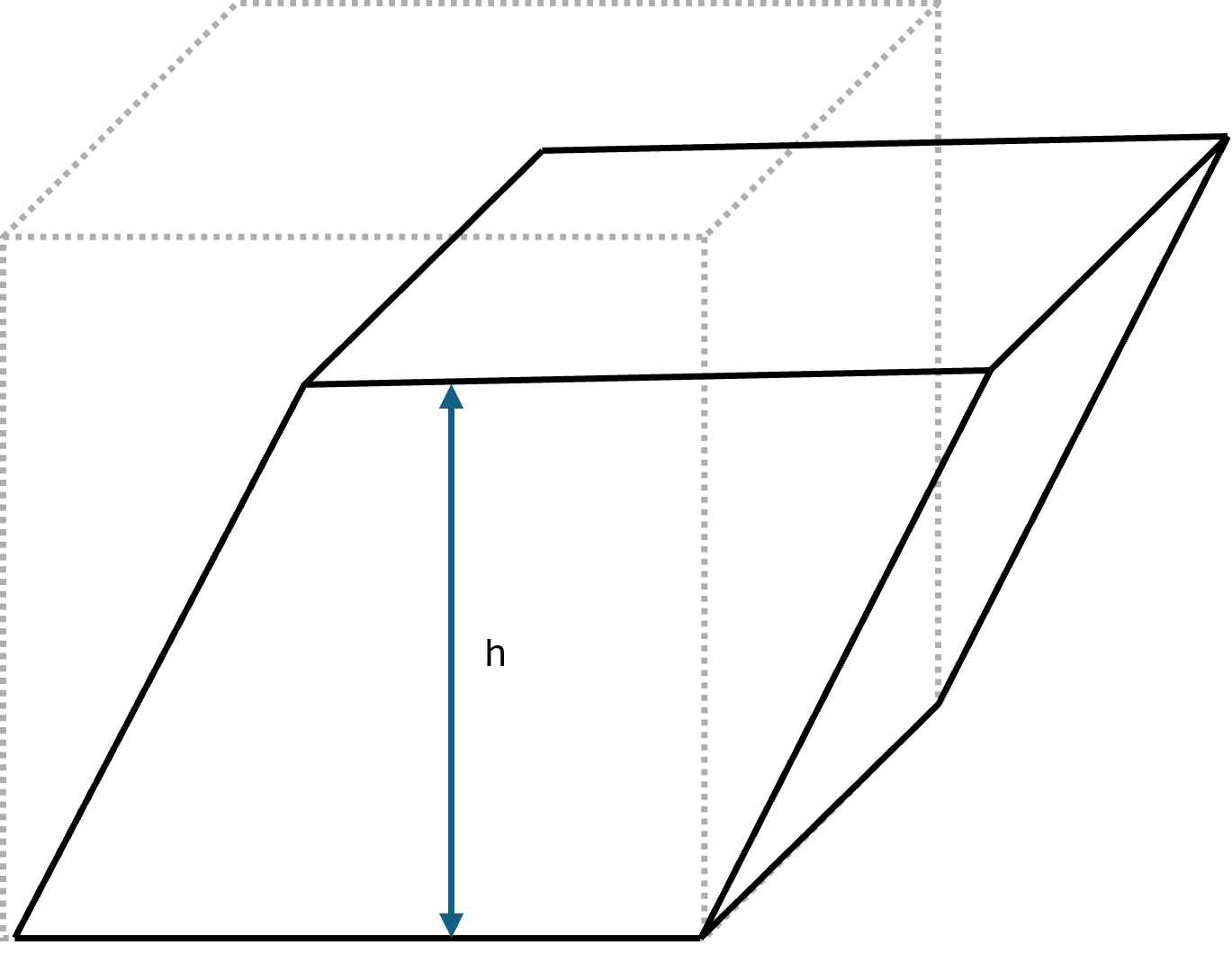
Suppose we have a cube where the base is a square with side length \( \large a = 4 \,\text{cm} \). The base area is therefore:
$$ \large A_{base} = 4^2 = 16 \,\text{cm}^2 $$
The slanted edge in the cube is \( \large s = 10 \,\text{cm} \), and the angle between this edge and the base is \( \large 45^\circ \). The actual height is found by:
$$ \large h = s \cdot \sin(45^\circ) $$
$$ \large h= 10 \cdot \tfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2} $$
$$ \large h \approx 7.07 \,\text{cm} $$
The volume is therefore:
$$ \large V = A_{base} \cdot h $$
$$ \large V = 16 \cdot 7.07 $$
$$ \large V \approx 113.1 \,\text{cm}^3 $$
Surface area
In a right cube the surface consists of six square faces, and therefore the simple formula applies:
$$ \large O = 6a^2 $$
In an oblique cube the bases are still squares, but the side faces become parallelograms instead of squares.
The surface area is therefore found by summing the areas of all six faces:
$$ \large O = 2a^2 + 4 \cdot (a \cdot h_{\text{side}}) $$
Here \( \large h_{\text{side}} \) is the height of the parallelograms that form the side faces of the cube. It depends on the angle between the side length and the base.